World cities - role of cities
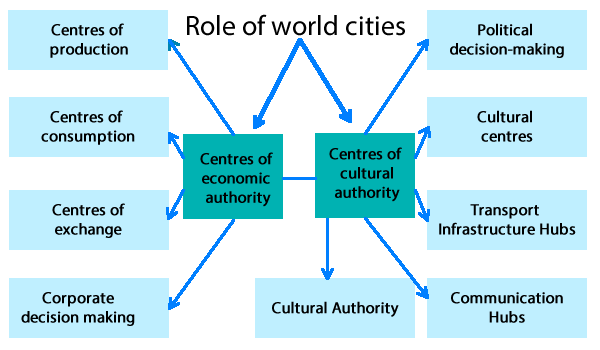
Centres of economic authority
World cities are intrinsically linked to globalisation. Globalisation is the development of stronger links between countries and the breaking down of any existing barriers as a result of technological communication.
Centres of Production
- major manufacturing centres with up-to-date port facilities, e.g. container wharves.
- centre of wholesaling
- specialised industrialised zones
- lots of production has been outsourced to developing countries.
- facilities - ports, specialised cargo terminals, freight train lines, motorways.
Centres of Consumption
- dominate trade and the economy of surrounding areas (sometime the surrounding regional and sometimes internationally).
- centre of retailing
- large markets for expensive, designer products and a vast range of goods and services
Centres of Exchange/ Financial centres
- centres for banking and other financial services.
- the largest banks in the world have their headquarters located in world cities. For example: New York, Citigroup and Chase Manhattan; London, HSBC Holdings and Barclays PLC; and Tokyo, Bank of Tokyo, Mitsubishi and Dai-Ichi Bank.
- all of the major stock exchanges are located in world cities, for example 'Wall Street' in New York.
- major financial companies are located in world cities.
- centre of banking, foreign exchange, investment capital, equities and bonds.
- leading global markets for commodities and commodity futures
Corporate Decision-making
- Head quatres of TNCs - World cities are often the basis of transnational and national corporations that greatly influence the global economy, and particularly dominate world trade. They decide where, when and how much production of a particular product takes place.
concentrations of national firms and large foreign firms
- specialised high-order business services - law, property, advertising, etc
- finance and corporate management
Centres of Production
- major manufacturing centres with up-to-date port facilities, e.g. container wharves.
- centre of wholesaling
- specialised industrialised zones
- lots of production has been outsourced to developing countries.
- facilities - ports, specialised cargo terminals, freight train lines, motorways.
Centres of Consumption
- dominate trade and the economy of surrounding areas (sometime the surrounding regional and sometimes internationally).
- centre of retailing
- large markets for expensive, designer products and a vast range of goods and services
Centres of Exchange/ Financial centres
- centres for banking and other financial services.
- the largest banks in the world have their headquarters located in world cities. For example: New York, Citigroup and Chase Manhattan; London, HSBC Holdings and Barclays PLC; and Tokyo, Bank of Tokyo, Mitsubishi and Dai-Ichi Bank.
- all of the major stock exchanges are located in world cities, for example 'Wall Street' in New York.
- major financial companies are located in world cities.
- centre of banking, foreign exchange, investment capital, equities and bonds.
- leading global markets for commodities and commodity futures
Corporate Decision-making
- Head quatres of TNCs - World cities are often the basis of transnational and national corporations that greatly influence the global economy, and particularly dominate world trade. They decide where, when and how much production of a particular product takes place.
concentrations of national firms and large foreign firms
- specialised high-order business services - law, property, advertising, etc
- finance and corporate management
Centres of cultural authority
Political decision-making
- World cities are the location of decision-making regionally and often nationally.
- Centres of Non-Government Organisations (NGOs), e.g. Amnesty International. Play an important role in addressing humanitarian and environmental issues.
- Centres of International Organisations, e.g. World Trade Organisation (New York), OECD (Paris).
government services
- Parliament buildings are located in world cities, and as such political decisions are made in these cities.
Cultural centres
- Culturally, world cities have many historical, cultural and scenic activities for tourists and residents.
- World cities usually have fine theatres, opera houses, and museums which host large cultural events such as art exhibitions and sporting venues hosting major sporting tournaments.
- Centres of new ideas and innovation
Transport Infrastructure Hubs
- fast air connections
- hubs of national road and rail networks
- major airports (Heathrow, London)
- direct flights between other world cities
- major ports close to world cities aid trade
- shipping lanes
- rail transport allows movement of people to surrounding areas and sometimes internationally (Eurail).
- transport networks also connect other major cities and a variety of urban and rural centres.
Communication Hubs
- Key locations of media organisations - news, information services, cultural industries
- concentration of electronic exchange pot information
- Major tourist attractions
- centres of media and communications for global networks
- telecommunications networks have been revolutionised by satellites.
- The global telephone network is dominated by world cities e.g. most outgoing and incoming telephone calls
Cultural Authority
- large number of people employed in tertiary and quaternary industries - highly skilled
- legal, medical, education, entertainment facilities.
- sophisticated and varied social activities
- prestigious lifestyles, housing, entertainment
- ability to influence specific cultural processes
- facilitate social and cultural interactions
- Cultural, sporting and entertainment centres (e.g. Lourve in Paris and La Scala Opera House in Milan)
Groupwork activity: Roles of World Cities
Each pair will focus on one specific role of world cities. You will be given a table to fill in which requires the following information about your role:
Description (What is the role? What does it mean?)
Key aspects (What are the important features of the role?)
Examples (What are specific cities the demonstrate this and how do they demonstrate this?)
Description (What is the role? What does it mean?)
Key aspects (What are the important features of the role?)
Examples (What are specific cities the demonstrate this and how do they demonstrate this?)